Products Category
- FM Transmitter
- 0-50w 50w-1000w 2kw-10kw 10kw+
- TV Transmitter
- 0-50w 50-1kw 2kw-10kw
- FM Antenna
- TV Antenna
- Antenna Accessory
- Cable Connector Power Splitter Dummy Load
- RF Transistor
- Power Supply
- Audio Equipments
- DTV Front End Equipment
- Link System
- STL system Microwave Link system
- FM Radio
- Power Meter
- Other Products
- Special for Coronavirus
Products Tags
Fmuser Sites
- es.fmuser.net
- it.fmuser.net
- fr.fmuser.net
- de.fmuser.net
- af.fmuser.net ->Afrikaans
- sq.fmuser.net ->Albanian
- ar.fmuser.net ->Arabic
- hy.fmuser.net ->Armenian
- az.fmuser.net ->Azerbaijani
- eu.fmuser.net ->Basque
- be.fmuser.net ->Belarusian
- bg.fmuser.net ->Bulgarian
- ca.fmuser.net ->Catalan
- zh-CN.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Simplified)
- zh-TW.fmuser.net ->Chinese (Traditional)
- hr.fmuser.net ->Croatian
- cs.fmuser.net ->Czech
- da.fmuser.net ->Danish
- nl.fmuser.net ->Dutch
- et.fmuser.net ->Estonian
- tl.fmuser.net ->Filipino
- fi.fmuser.net ->Finnish
- fr.fmuser.net ->French
- gl.fmuser.net ->Galician
- ka.fmuser.net ->Georgian
- de.fmuser.net ->German
- el.fmuser.net ->Greek
- ht.fmuser.net ->Haitian Creole
- iw.fmuser.net ->Hebrew
- hi.fmuser.net ->Hindi
- hu.fmuser.net ->Hungarian
- is.fmuser.net ->Icelandic
- id.fmuser.net ->Indonesian
- ga.fmuser.net ->Irish
- it.fmuser.net ->Italian
- ja.fmuser.net ->Japanese
- ko.fmuser.net ->Korean
- lv.fmuser.net ->Latvian
- lt.fmuser.net ->Lithuanian
- mk.fmuser.net ->Macedonian
- ms.fmuser.net ->Malay
- mt.fmuser.net ->Maltese
- no.fmuser.net ->Norwegian
- fa.fmuser.net ->Persian
- pl.fmuser.net ->Polish
- pt.fmuser.net ->Portuguese
- ro.fmuser.net ->Romanian
- ru.fmuser.net ->Russian
- sr.fmuser.net ->Serbian
- sk.fmuser.net ->Slovak
- sl.fmuser.net ->Slovenian
- es.fmuser.net ->Spanish
- sw.fmuser.net ->Swahili
- sv.fmuser.net ->Swedish
- th.fmuser.net ->Thai
- tr.fmuser.net ->Turkish
- uk.fmuser.net ->Ukrainian
- ur.fmuser.net ->Urdu
- vi.fmuser.net ->Vietnamese
- cy.fmuser.net ->Welsh
- yi.fmuser.net ->Yiddish
An Ultimate Guide to Zener Diodes in 2021

A Zener diode is highly useful when it comes to regulating and stabilizing variations in load or supply against a voltage source and other applications. What do you know about the Zener diode?
This guide will introduce the definition of a Zener Diode, its characteristics, specifications, applications, how it works, and its symbol in the circuit diagram. If you are an electronics enthusiast or come into contact with Zener Diode at work, you can have a better understanding of the Zener Diode through this share. Let's keep reading!
Sharing is Caring!
Content
● 3 Main Characteristics of a Zener Diode
● Specifications of a Zener Diode
● What are the Applications of a Zener Diode?
● What is the Zener Diode Symbol?
● FAQ
Zener diodes are silicone-based discrete semiconductor devices which allow current to flow bidirectionally - either reverse or forward. Diodes are comprised of a heavily-doped P-N silicone junction, which is intended to conduct in the reverse direction once a particular voltage threshold has been met.
Zener diodes have a set reverse breakdown voltage. When this is reached, they start to conduct current and continue to operate unceasingly in the reverse bias direction without incurring damage. One of the main benefits of Zener diodes is that a varying range of voltages will still maintain a constant voltage drop across the diode. As a result, Zener diodes can be used for voltage regulation applications.
The Introduction to Zener Diodes that Explaining How They Work
3 Main Characteristics of a Zener Diode
Zener diodes operate similarly to conventional diodes when in the forward-bias mode.
● They have a bias turn-on voltage of between 0.3 and 0.7V. When connected in the reverse mode, there is a small leakage current flow in most applications.
● As the reverse voltage increases to the set breakdown voltage, there will be current flowing through the diode. When the current increases to a maximum (determined by the resistors in series), it will then stabilise and remain constant over a wide range of applied voltage.
● Irrespective of the current value flowing through the diode, the voltage remains almost constant. This is also the case with large current changes, providing that the diode current stays between the maximum current and the breakdown current.
A Zener diode’s strong self-control is highly useful when it comes to regulating and stabilising variations in load or supply against a voltage source. This makes it a key characteristic as it enables the diode to be used in a variety of voltage regulator applications.
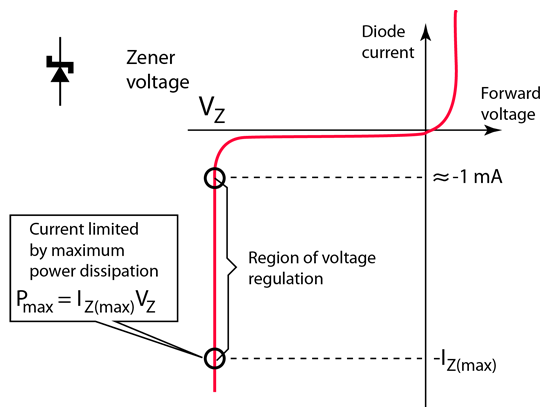
Specifications of a Zener Diode
Some specifications will vary between individual Zener diodes. These include power dissipation, nominal working voltage, and maximum reverse current. Additional commonplace specifications include:
● Zener Voltage - this relates to the reverse breakdown voltage. This ranges from 2.4V up to 200V, depending on the specific diode
● Current (maximum) - the maximum current at the rated Zener voltage. This can range from 200uA to 200A
● Current (minimum) - the minimum current required at the Zener voltage for the diode to break down. This is typically between 5mA and 10mA
● Power Rating - the maximum power dissipation rating of the diode, including both the current flowing through the diode and the voltage across it. Standard values include 400mW, 500mW, 1W, and 5W. With surface-mounted diodes, typical values are 200mW, 350mW, 500mW, and 1W
● Voltage Tolerance - typically ±5%
● Temperature Stability - the most stable diodes are usually approximately 5V
● Zener Resistance - the resistance exhibited by the diode
What are the Applications of a Zener Diode?
Zener diodes are used for a range of applications, including:
● Voltage regulation
● Voltage reference
● Surge suppression
● Switching applications
● Clipper circuits
It is possible to use a Zener diode to create a stabilised low-ripple output voltage under variable load current conditions. When a suitable current limiting resistor is used to pass a minor current from a voltage source through the diode, sufficient current will be conducted to maintain the required voltage drop. As the load value is altered, the average voltage output also changes. However, the addition of a Zener diode can produce an even voltage output.
With that being said, it should also be noted that Zener diodes may occasionally produce electrical noise on the DC supply as they work to steady the voltage. This is fine in the majority of applications, but adding a high value decoupling capacitor to the output of the diode can rectify the problem by providing extra smoothing.
As Zener diodes can operate in the reverse bias condition, they can be used in voltage regulator circuits to sustain constant DC voltage output. This constant voltage can be maintained despite any variations in voltage input or load current changes.
This voltage regulator circuit comprises a current limiting resistor which is connected in series with the input voltage. The diode and the load should then be connected in parallel. The stabilised voltage output and the diode’s breakdown voltage will always be the same.
The principle behind the operation of a Zener diode is determined by the cause of the diode’s breakdown in the reverse bias condition. There are typically two types – Zener breakdown and avalanche breakdown.
Zener Breakdown
A Zener breakdown happens with a reverse bias voltage between 2V and 8V. The intensity of the electric field is enough to apply force to the valence electrons, separating them from the nuclei – even at this low voltage. This process forms mobile electron-hole pairs, therefore increasing current flow.
Zener breakdowns typically occur for highly-doped diodes with a large electric field and low breakdown voltage. More energy is gained by the valence electrons as temperature increases, therefore requiring less outward voltage. This also means that Zener breakdown voltage reduces alongside temperature.
Avalanche Breakdown
Voltage breakdown also happens in the reverse bias condition, at a minimum of 8V, for light-doped diodes that have a large breakdown voltage. Electrons flowing through the diode collide with electrons in the covalent bond, disrupting it.
The velocity of the electrons increases as the voltage also increases, meaning that the covalent bonds can be disrupted more easily. It should also be noted that avalanche breakdown voltage rises alongside temperature.
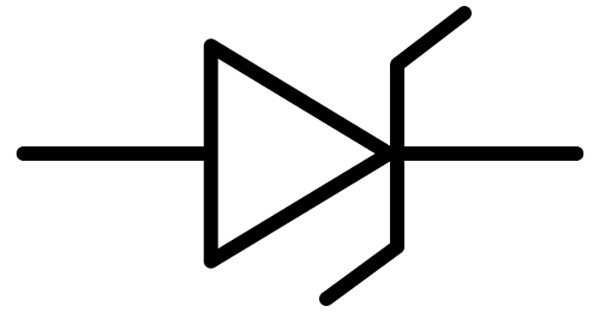
What is the Zener Diode Symbol?
The images below portray the standard Zener diode symbol used within a circuit diagram. This symbol shows how the presence of a Zener diode would be noted in a circuit diagram. Similarly, if you see this symbol in a circuit diagram, it means that a Zener diode is present at that point in the circuit.
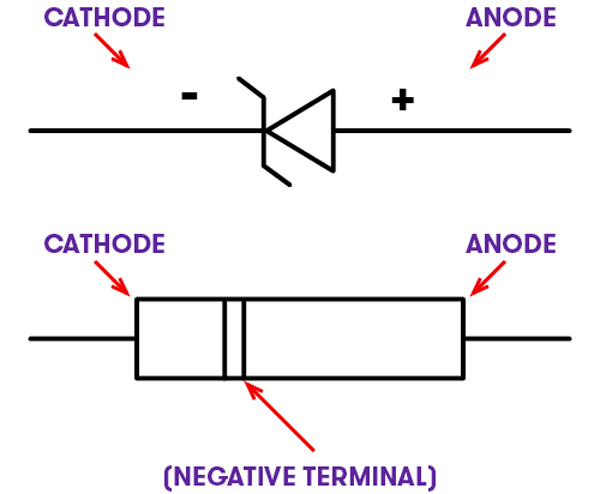
This diagram then builds on the above, showing more information about the Zener diode. The top line of the diagram shows the diode symbol plus the positive and negative as it relates to the anode and cathode. The bottom line of the diagram shows the same, except with a simplified version of a realistic diode as opposed to the Zener diode symbol.
1. Q: Can Multiple Zener Diodes be Connected in Series?
A: Multiple zener diodes can be connected in series, usually to achieve a specific zener voltage. However, if you use multiple diodes, you must also monitor the Zener Current and ensure that the maximum value is not exceeded.
This is because the maximum Zener Current allowed is equal to the lowest diode connected in series. This also means that when two zener diodes are connected in series, if the diodes do not have the same Zener Current specification, they will not show the specified Zener Current or voltage.
2. Q: What is the Difference Between Zener Diode and Diode?
A: Diode is a unidirectional (unidirectional) conductive semiconductor device. Zener diodes are also semiconductor devices, but the key difference is that they can conduct electricity under forward and reverse bias conditions.
Another important difference between the two types is doping intensity. Traditional diodes are usually moderately doped, while zener diodes are more doped to achieve higher breakdown voltage.
3. Q: Where are Zener Diodes Used?
Zener diode is widely used in various electronic devices and is one of the basic components of electronic circuits. They are used to generate a low-power stable power rail from a higher voltage and provide a reference voltage for the circuit, especially a stable power supply such as building in a DC / DC regulator for overvoltage protection.
4. Q: What are the Advantages of Zener Diodes?
Zener diode is cheaper than another diode. The diode can be used to adjust and stabilize the voltage in the circuit. These diodes have high performance standards. Control the current flowing.
Speaking of which, we learn the basic information about Zener diode, including its definition, characteristics, specifications, applications, how does it work, and how is it noted in a circuit diagram. Having a better understanding of the Zener diode can help you make better use of them in the regulating voltage circuit. What do you think about the Zener Diode? Leave your comments below and we will reply you as soon as possibile. If you think this share is helpful for you, don't forget to share it!
Also Read
● Things You Should Not Miss About Facebook Meta and Metaverse
● What's the Difference between AM and FM?
● How LTM8022 μModule Regulator Provides a Better Design for Power Supply?
● How to Detect Zener Diode Based Voltage Regulators?

